It tends to create a market surplus because the quantity supplied at the price floor is higher than the quantity demanded.
A government imposed price floor in a particular market.
Similarly a typical supply curve is.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
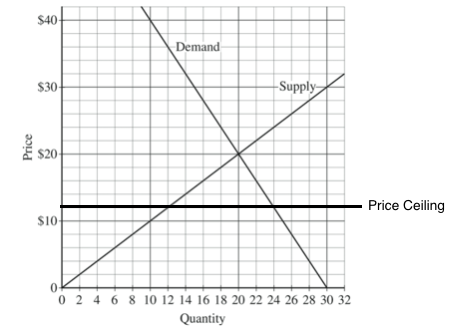
Consumers would wish to purchase 1 000 compact discs.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
Demand curve is generally downward sloping which means that the quantity demanded increase when the price decreases and vice versa.
There would be a surplus of 4 000 compact discs.
A price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at.
The quantity supplied at the market price equals the quantity demanded at that price.
If the government imposes a price floor of 25 for compact discs which of the following will be true.
Producers would wish to sell 5 000 compact discs.
Market interventions and deadweight loss.
Although both a price ceiling and a price floor can be imposed the government usually only selects either a ceiling or a floor for particular goods or services.
A price floor is a minimum price enforced in a market by a government or self imposed by a group.
Price ceilings and price floors.
It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price.
Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government.
Figure 4 1 illustrates the market for compact discs.
Example breaking down tax.
Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers.
Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low.
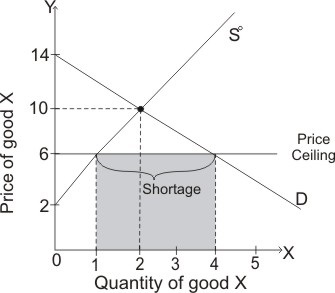
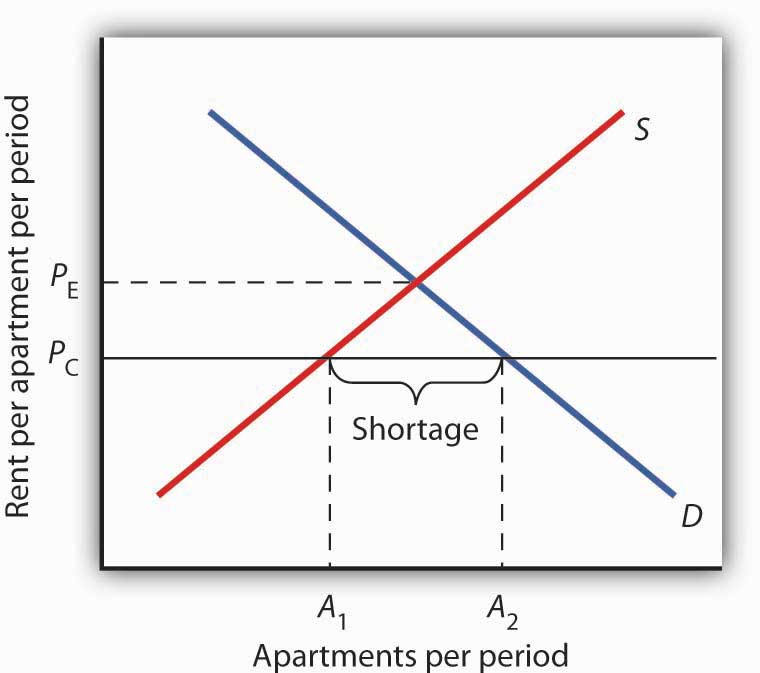
However when a government imposes price controls the eventual consequence can be the creation of excess demand in the case of price ceilings or excess supply in the case of price floors.
How price controls reallocate surplus.
All of the above are true.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
A price floor if set above the market equilibrium price means consumers will be forced to pay more for that good or service than they would if prices were set on free market principles.
Rent control and deadweight loss.
If for example a crop had a market price of 3 per unit and a target price of 4 per unit the government would give farmers a payment of 1 for each unit sold.
But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.
When prices are established by a free market then there is a balance between supply and demand.
If the average market price for a crop fell below the crop s target price the government paid the difference.
This is the currently selected item.
Minimum wage and price floors.